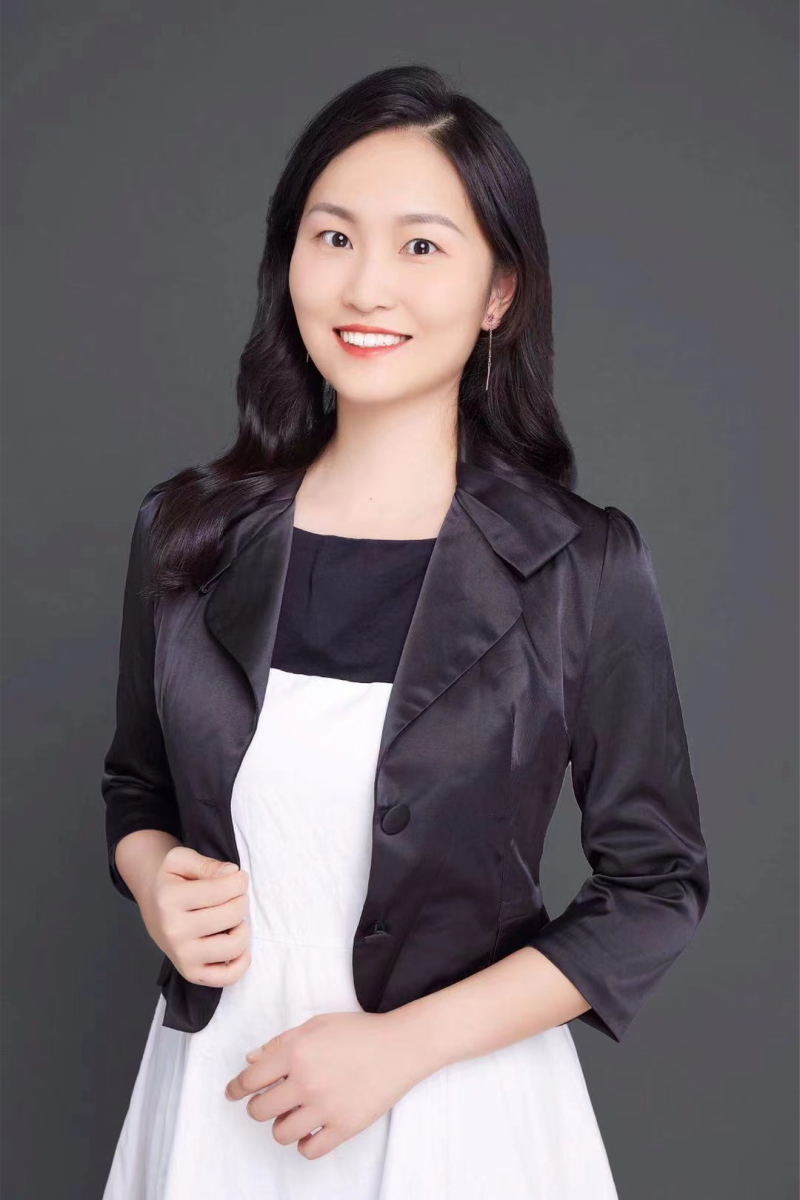

林苡 长聘教轨助理教授
部门:本科生公共英语教学中心
邮箱:carol.y.lin@sjtu.edu.cn
 主要经历
主要经历
林苡,bwin必赢唯一官方网站长聘教轨副教授,硕士生导师,bwin必赢唯一官方网站外国语言文学博士。研究方向为实验语音韵律学、语言认知神经科学、英语教育,主要从事健康和障碍人群多模态言语和情感加工的认知神经机制研究,在语言学、心理学、医学类高水平SCI/SSCI期刊和EI国际会议上发表论文20余篇,主持国家社科基金青年项目、上海市晨光计划等课题。获全国高等院校英语教师教学基本功大赛微课组二等奖、bwin必赢唯一官方网站优秀博士学位论文、bwin必赢唯一官方网站“学术之星”等荣誉。现担任Psychology and Aging期刊的编委。
 教学科研
教学科研
一、教学
(一) 课程教学
承担以下课程的教学工作:
- 强化英语1 (医学院): 2022秋、2023 秋
- 大学英语3(致远学院、法学院等): 2023 春、2024秋、2025春
- 学术英语写作与交际: 2023 夏、2025夏
- 英语读写1(体育明星班):2023秋
- 大学英语2(体育明星班):2025春
- 大学英语4(致远学院): 2024 春
- 英语口语基础(全校公选课):2024夏、2024秋、2025秋
- 听力科学:2024秋
- 跨文化交际:2025秋
(二)教材与教学案例
- 张荔、韦瑶瑜、黄爱军、林铃、林苡、郁杨洋. (2025). 《学术英语演讲(视听说教程)》,bwin必赢唯一官方网站出版社.
- 林苡, 2024, 大学英语(5)学术英语写作与演讲课程思政教学案例:积极乐观. 张荔(编),《外语课程思政教学与研究》. 北京: 光明日报出版社, 209–219.
(三)获奖情况
- 全国高等院校英语教师教学基本功大赛微课组二等奖
- “外教社杯”全国高校外语教学大赛上海赛区大学英语视听说课组二等奖
- 上海市外语微课优秀作品征集与交流活动二等奖
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站研究生教学成果一等奖《语言与沟通障碍科学本硕博人才贯穿培养改革与实践》(排8)
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站第七届青年教师教学比赛三等奖
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站科研贡献奖一等奖、年度考核优秀(2023年)
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站优秀班主任
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站青年教师教学比赛“最佳教学奖”
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站淩鸿勋奖教金
- The Best Paper Award in the 2nd Conference on Data Science and L2 Studies
(四)指导学生
硕士生导师,招收硕士生、本科生开展科研项目和毕业论文研究,指导学生获评:
- 全国医学英语词汇竞赛二等奖
- 上海市“挑战杯”大学生课外学术科技作品竞赛特等奖
- “中国国际大学生创新大赛”上海赛区决赛金奖
- 上海市大学生职业生涯规划大赛铜奖
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站第六届学生职业生涯规划大赛一等奖(第一名)
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站“盛宣怀杯”第二十六届创新创业大赛金奖
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站第三届“唐文治”杯哲学社会科学类课外学术科技作品竞赛一等奖、二等奖、最佳人气奖
累计指导:
- 国家级大学生创新项目2项
- 上海市级大学生创新项目1项
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站䇹政项目2项
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站大学生创业训练计划
- bwin必赢唯一官方网站本科生PRP项目(获评优秀项目)
二、科研
(一) 研究方向
研究兴趣包括实验语音韵律学、认知神经语言学、病理语言学、语言习得与教学,目前主要从事以下方向的研究:
- 健康和特殊人群(包括老年人、精神分裂症患者、儿童等)多模态语音韵律加工
- 视听情绪信息整合的认知神经机制
- 人工智能辅助口语和写作的教学和学习
欢迎感兴趣的同学与我联系!
(二) 主要科研项目
- 主持国家社科基金青年项目《老年人多通道情绪语音解码的认知神经机制研究》(在研)
- 主持上海市晨光计划项目《老年人言语情绪的视听多模态加工机制研究》(在研)
- 主持bwin必赢唯一官方网站文科青年人才培育项目《情绪语音感知中的老化机制研究》(在研)
- 主持bwin必赢唯一官方网站“人工智能+教育”专项课题《AI助教在大学英语口语教学中的应用与效果研究》(良好结项)
- 主持bwin必赢唯一官方网站优秀青年教师奖励计划(2025-2027,在研)
- 主持bwin必赢唯一官方网站“AI+外语专业”课程建设项目《听力科学》(在研)
(三)学术论文
- Lin Y. (2025). Multisensory Stroop effects in emotional speech perception: Age-related changes and cognitive links. Psychology and Aging, 10.1037/pag0000933. Advance online publication. (SSCI indexed, Gerontology, Psychology Q1,IF = 3.7)
- Lin, Y., Lu, G., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Similarities and differences in neural processing of emotional prosody in speech and nonspeech contexts. Language, Cognition and Neuroscience, 1–19. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.3)
- Lin, Y., Lu, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Relative advantages of speech vs. nonspeech in emotion perception: Effects of emotional category and attentional focus. Current Psychology. (SSCI indexed, Psychology Q1, IF = 2.9)
- Lin, Y., Xu, F., Ye, X., Zhang, H., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Age and sex differences in emotion perception are influenced by emotional category and communication channel. Psychology and Aging, 40(1), 17-31. (SSCI indexed, Gerontology, Psychology Q1,IF = 3.7)
- Lin, Y., Ni, S., & Lu, Y. (2025). Age-related changes in multisensory integration of emotions in an audiovisual face-prosody-semantics Stroop task. Paper presented at the Interspeech 2025. (EI indexed)
- Lin, Y., Ye, X., Zhang, H., Xu, F., Zhang, J., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Category-sensitive age-related shifts between prosodic and semantic dominance in emotion perception linked to cognitive capacities. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 67(12), 4829-4849. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Fan, X., Tang, E., Zhang, M., Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Decline of affective prosody recognition with a positivity bias among older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 67(10), 3862-3879. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Lin, Y., Li, C., Hu, R., Zhou, L., Ding, H., Fan, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Impaired emotion perception in schizophrenia shows sex differences with channel- and category-specific effects: A pilot study. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 161, 150-157. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Psychiatry Q1, IF = 5.95)
- Lin, Y., Li, C., Wang, X., Song, Y., Ding, H., Fan, Q., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Channel- and category-specific emotion recognition deficits and their associations with symptomatology and cognition in individuals with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 254, 37-39. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Psychiatry Q1, IF = 4.2)
- Lin, Y., Fan, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, H., Chen, F., Zhang, H., . . . Zhang, Y. (2022). Neurocognitive dynamics of prosodic salience over semantics during explicit and implicit processing of basic emotions in spoken words. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1706. (SCI indexed, Neuroscience Q3,IF = 3.33)
- Lin, Y., Li, C., Fan, Q., Chen, Y., Zhang, J., & Ding, H. (2022). Effects of sensory dominance and gender differences on impaired emotion perception in schizophrenic patients. Speech Prosody 2022. (EI indexed)
- Tang, E., Zhang, M., Chen, Y., Lin, Y., & Ding, H. (2022). Recognition of affective prosody in bipolar and depressive conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 313, 126-136. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Psychiatry Q1, IF = 6.53)
- Zhang, M., Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2022) Multichannel perception of emotion in speech, voice, facial expression, and gesture in individuals with autism: A scoping review. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 65(4), 1435-1449. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Gender differences in identifying facial, prosodic, and semantic emotions show category- and channel-specific effects mediated by encoder’s gender. Journal of Speech, Language & Hearing Research, 64(8), 2941-2955. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Unisensory and multisensory Stroop effects modulate gender differences in verbal and nonverbal emotion perception. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 64(11), 4439-4457. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Lin, Y., Fan, X., Zhang, H., Chen, F., Zhang, H., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Communication channel, emotion category and attentional requirement modulate emotional speech perception: Electrophysiological and behavioral evidence. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 150(4), A274. (SCI indexed, IF = 1.84)
- Zhang, M., Xu, S., Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Recognition of affective prosody in autism spectrum conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Autism. 26(4), 798-813. (SSCI indexed, Psychology Q1, IF = 7.271)
- Gao, Y., Ding, H., Birkholz, P., & Lin, Y. (2021). Comparing fundamental frequency of German vowels produced by German native speakers and Mandarin Chinese learners. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America Express Letters, 1(7). (SCI indexed, Acoustics Q2, IF = 1.84)
- Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Prosody dominates over semantics in emotion word processing: Evidence from cross-channel and cross-modal Stroop effects. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 63(3), 896-912. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Linguistics Q1, IF = 2.86)
- Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Multisensory integration of emotion in schizophrenic patients. Multisensory Research, 1-37. (SCI/SSCI indexed, Psychology Q3, IF = 2.02)
- Lin, Y., & Ding, H. (2020). Effects of communication channels and actor’s gender on emotion identification by native Mandarin speakers. Paper presented at the Interspeech 2020. (EI indexed)
- Lin, Y., & Ding, H. (2019, October 14 - 18, 2019). Multisensory integration of emotions in a face-prosody-semantics Stroop task. Paper presented at the ICMI '19 NeuroManagement and Intelligent Computing Method on Multimodal Interaction, Suzhou, China. (EI indexed)
- Lin, Y., Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Li, C. (2019). Speech databases for mental disorders: A systematic review. General Psychiatry, 32(3), e100022. (ESCI indexed)
- Gao, Y., Ding, H., Birkholz, P., Jäckel, R. & Lin, Y. (2019). Perception of German tense and lax vowel contrast by Chinese learners. Studientexte zur Sprachkommunikation, 93, 25-32.
- Lin, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Emotional prosody processing in schizophrenic patients: A selective review and meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(10). 363. (SCI indexed, Clinical Medicine Q1, IF = 5.69)
- Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Zelchenko, P., Cui, X., Lin, Y., Zhan, Y., & Zhang, H. (2018). Prosodic disambiguation by Chinese EFL learners in a cooperative game task. Paper presented at the 9th International Conference on Speech Prosody 2018. (EI indexed)
三、社会服务
创设融党团建设、科研科普、人才培养和社会服务于一体的“老年听力认知公益项目”,累计举办50余期公益活动,从闵行区江川路街道逐步拓展至杨浦、虹口、静安等上海市多个区域,并辐射至西藏、安徽等地,实践活动入选教育部“推普助力乡村振兴”全国大学生暑期社会实践志愿服务重点项目和bwin必赢唯一官方网站暑期社会实践重点项目,团队学生获bwin必赢唯一官方网站“十佳志愿者”和“十佳公益组织”荣誉。活动事迹受人民网、青春上海等主流媒体的报道。
 社会兼职
社会兼职
- Psychology and Aging 期刊编委
- 担任20余本国际期刊和会议审稿人,包括Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research、Psychology and Aging、Journal of Phonetics、Current Psychology、Cerebral Cortex、Speech Communication、Cognitive Neurodynamics 、Language and Speech 、Lingua 、National Conference on Man-Machine Speech Communication、Interspeech Conference 等
- 中国老年学和老年医学学会成员
- 广东省卫生信息网络协会智慧心理健康分会委员会委员
- International Speech Communication Association成员
- Speech Prosody Special Interest Group 成员

 ENGLISH
ENGLISH 教师登录
教师登录
 地址:中国上海东川路800号bwin必赢唯一官方网站闵行校区杨咏曼楼
地址:中国上海东川路800号bwin必赢唯一官方网站闵行校区杨咏曼楼 邮编:200240
邮编:200240  网址:http:
网址:http: 电话:021-34205664 (党政办公室)
电话:021-34205664 (党政办公室) 